WEDNESDAY, MARCH 8, 2017
A research group in China recently made a discovery that may help in the development of new anti-corrosion coatings.
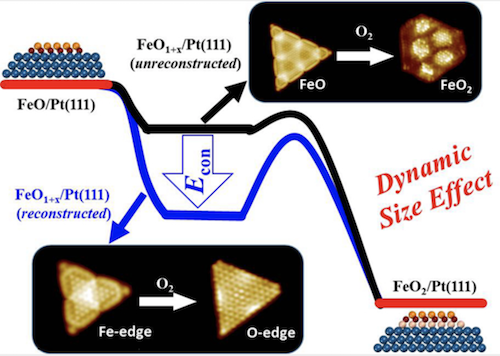
In the study first published in Nature Communications, researchers found that oxide nanostructures with a diameter smaller than 3 nanometers could exhibit better oxidation resistance over larger nanostructures.
Previously there has been a limited understanding of the underlying mechanism of oxidation in nanostructures with diameters smaller than 5 nanomaters because they have rarely been studied.
However, by investigating the oxidation mechanism at the atomic level, the team—led by professors Bao Xinhe and Yang Fan from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences—has proposed that a “dynamic size effect” determines the stability of supported nanoparticles.
 |
| Yang Fan |
|
In the study first published in Nature Communications, researchers found that oxide nanostructures with a diameter smaller than 3 nanometers could exhibit better oxidation resistance over larger nanostructures. |
The research not only helps in understand the dynamic remodeling mechanism of nanocatalysts in oxygen, but also provides a new interface control for the development of an anti-corrosion and anti-oxidation nano-protective coating.
The Findings
The study showed that iron oxide nanostructures smaller than 3.2 nanometers could undergo a complete reconstruction, when oxygen dissociates at the coordinative unsaturated ferrous centers at the edges of FeO nanostructures. Accompanying the reconstruction, the dissociated oxygen atoms are stabilized at the edges of FeO nanostructures and could not penetrate the interface FeO and Pt, thereby inhibiting the further oxidation of FeO nanostructures. FeO nanostructures larger than 3.2 nanometers oxidize more easily because of their inability to complete the reconstruction.
Previously, several nanocrystalline materials were also reported to exhibit improved oxidation resistance with respect to bulk materials and have been applied as anti-corrosion coatings.
Tagged categories: Coating chemistry; Coating Materials; Coating Materials; Coating types; Corrosion protection; Iron oxide pigments; Nanotechnology
By using the PaintSquare.com service, you accept its terms. We may change the terms of this agreement from time to time. By continuing to use the service after we post any such changes, you accept this agreement, as modified.
If you are an owner of intellectual property who believes your intellectual property has been improperly posted or distributed via this web site, please notify us, by e-mail, to webmaster@paintsquare.com.
The material that appears on PaintSquare.com is for informational purposes only. Despite our efforts to provide useful and accurate information, errors may appear from time to time. Before you act on information on PaintSquare.com, you should confirm any facts that are important to your decision. Technology Publishing / PaintSquare is not responsible for, and cannot guarantee the performance of, goods and services provided by our advertisers or others to whose sites we link. A link to another web site does not constitute an endorsement of that site (nor of any product, service, or other material offered on that site) by Technology Publishing / PaintSquare.
Technology Publishing / PaintSquare reserves the right (but assumes no obligation) to delete, move, or edit any postings to the site considered unacceptable or inappropriate for legal or other reasons. Technology Publishing / PaintSquare will not, in the ordinary course of business, review private electronic messages that are not addressed to Technology Publishing / PaintSquare. However, we will comply with the requirements of the law regarding disclosure of such messages to others, including law enforcement agencies.
Technology Publishing / PaintSquare does not make any representation as to the accuracy or suitability of any of the information contained in third-party advertisements or sites and does not accept any responsibility or liability for the conduct or content of those advertisements, sites or the offerings made by the third parties. Technology Publishing / PaintSquare takes no responsibility for a third-party link's operation or content and does not explicitly or implicitly endorse third-party advertisements. Third-party advertising in no way influences editorial content, products or services. The inclusion of advertising, logos or website links, or reference to any third-party products, process, service, trade name, trademark or manufacturer is not an endorsement by Technology Publishing / PaintSquare.
Technology Publishing / PaintSquare expects that you will not use the service to violate anyone's copyright, trademark, or other intellectual property rights. By submitting material to PaintSquare.com, you are representing that you are making your submission with the express consent of the owner. Submitting material that is the property of another, without the consent of its owner, is not only a violation of this agreement but may also subject you to legal liability for infringement of copyright, trademark, or other intellectual property rights.
Although we make PaintSquare.com publicly accessible, we don't intend to give up our rights, or anyone else's rights, to the materials appearing on the service. The materials available through PaintSquare.com are the property of Technology Publishing / PaintSquare, Southside Holdings, and/or its licensors, and are protected by copyright, trademark, and other intellectual property laws. You are free to display and print for your personal, non-commercial use information you receive through PaintSquare.com, but you may not otherwise reproduce any of the materials without the prior written consent of the owner. You may not distribute copies of materials found on PaintSquare.com in any form (including by e-mail or other electronic means) without prior written permission from the owner. Requests for permission to reproduce or distribute materials found on PaintSquare.com should be sent to webmaster@paintsquare.com.
You agree not to use PaintSquare.com to advertise or to solicit anyone to buy or sell products or services or to make donations of any kind without our express written approval.
From time to time, users post their e-mail addresses in public posting areas of the site. You agree not to gather these e-mail addresses for purposes of spamming.
PaintSquare.com welcomes links to our service. You are free to establish a hypertext link to this site so long as the link does not state or imply any sponsorship of your site by PaintSquare.com.
Without the prior written permission of Technology Publishing / PaintSquare, you may not frame any of the content of PaintSquare.com or incorporate into another web site or other service any intellectual property of Technology Publishing / PaintSquare or any of their licensors. Requests for permission to frame our content may be sent to webmaster@paintsquare.com.
You may not use any trademark or service mark appearing on PaintSquare.com without the prior written consent of the owner of the mark. "Technology Publishing / PaintSquare," "PaintSquare.com," and the PaintSquare, Paint BidTracker, JPCL, PaintSquare News, and Durability + Design logos are trademarks of Technology Publishing / PaintSquare.
To obtain access to many services on our site, you may be given an opportunity to register with PaintSquare.com. As part of any such registration process, you will select a user name and a password. You agree that the information you supply during that registration process will be accurate and complete and that you will not register under the name of, nor attempt to enter the service under the name of, another person. Technology Publishing / PaintSquare reserves the right to reject or terminate any user name that, in its judgment, it deems offensive. You will be responsible for preserving the confidentiality of your password and will notify PaintSquare.com's webmaster of any known or suspected unauthorized use of your account.
This visitor agreement has been made in and shall be construed in accordance with the laws of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. By using this service, you consent to the exclusive jurisdiction of the state and federal courts in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, in all disputes arising out of or relating to this agreement or this web site. By using PaintSquare.com, you agree to abide by the terms of this visitor agreement. We hope you enjoy using PaintSquare.com, and we welcome suggestions for improvements.
Please read this Disclaimer carefully before using PaintSquare.com
YOU AGREE THAT YOUR USE OF THIS SERVICE IS AT YOUR SOLE RISK. BECAUSE OF THE NUMBER OF POSSIBLE SOURCES OF INFORMATION AVAILABLE THROUGH THE SERVICE AND THE INHERENT HAZARDS AND UNCERTAINTIES OF ELECTRONIC DISTRIBUTION, THERE MAY BE DELAYS, OMISSIONS, INACCURACIES, OR OTHER PROBLEMS WITH SUCH INFORMATION. IF YOU RELY ON THIS SERVICE OR ANY MATERIAL AVAILABLE THROUGH THIS SERVICE, YOU DO SO AT YOUR OWN RISK. YOU UNDERSTAND THAT YOU ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY DAMAGE TO YOUR COMPUTER SYSTEM OR LOSS OF DATA THAT RESULTS FROM ANY MATERIAL AND/OR DATA DOWNLOADED FROM OR OTHERWISE PROVIDED THROUGH PAINTSQUARE.
THIS SERVICE IS PROVIDED TO YOU "AS IS," "WITH ALL FAULTS," AND "AS AVAILABLE." TECHNOLOGY PUBLISHING / PAINTSQUARE AND THEIR AFFILIATES, AGENTS, AND LICENSORS CANNOT AND DO NOT WARRANT THE ACCURACY, COMPLETENESS, CURRENTNESS, NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF THE INFORMATION AVAILABLE THROUGH THE SERVICE. NOR DO THEY GUARANTEE THAT THE SERVICE WILL BE ERROR-FREE, OR CONTINUOUSLY AVAILABLE, OR THAT THE SERVICE WILL BE FREE OF VIRUSES OR OTHER HARMFUL COMPONENTS.
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES SHALL TECHNOLOGY PUBLISHING / PAINTSQUARE OR THEIR AFFILIATES, AGENTS, OR LICENSORS BE LIABLE TO YOU OR ANYONE ELSE FOR ANY DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF USE OF PAINTSQUARE, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, OR SIMILAR DAMAGES, EVEN IF WE ARE ADVISED BEFOREHAND OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. (BECAUSE SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF CERTAIN CATEGORIES OF DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. IN SUCH STATES, THE LIABILITY OF TECHNOLOGY PUBLISHING / PAINTSQUARE AND THEIR AFFILIATES, AGENTS, AND LICENSORS IS LIMITED TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PERMITTED BY SUCH STATE LAW.) YOU AGREE THAT THE LIABILITY OF TECHNOLOGY PUBLISHING / PAINTSQUARE AND THEIR AFFILIATES, AGENTS, AND LICENSORS, IF ANY, ARISING OUT OF ANY KIND OF LEGAL CLAIM IN ANY WAY CONNECTED TO THE SERVICE SHALL NOT EXCEED THE AMOUNT YOU PAID TO THE SERVICE FOR THE USE OF THE SERVICE.
June 21, 2024
Technology Publishing / PaintSquare (TPC) is committed to protecting your privacy. This Privacy Statement applies to data collection and usage on PaintSquare.com sites and services. Please read the Privacy Statement below.
PaintSquare.com is an industry-focused website, intended for those involved with any and all phases of protecting steel and concrete structures with coatings. Personal information of all users is collected, used and disclosed as described in this Privacy Statement.
Other websites linked to or from the PaintSquare website have their own privacy statements that can be viewed on those sites; this Privacy Statement does not apply to linked and referenced sites.
TPC collects basic identity information, such as name and company, and personal contact information, such as email address, home or work address, telephone number and fax number. TPC may also collect demographic information, such as your state, ZIP code, country, company type, preferences, interests and favorite content. Information collected by TPC may be combined with information obtained via print publications, including but not limited to the Journal of Protective Coatings & Linings (JPCL) and PaintSquare Press.
If you choose to sign up for a paid subscription service (such as Paint BidTracker) TPC will collect additional personal information, including your credit card number and billing address, to create a TPC billing account.
TPC keeps track of the pages our customers visit within its websites to determine what TPC sites and services are the most popular. You may choose to not have the tracking include your user identification.
TPC also collects certain information about your computer hardware and software. This information may include: your IP address, browser type, domain names, access times and referring website addresses.
Certain TPC services may be co-branded and offered in conjunction with another company. If you register for or use such services, both TPC and the other company may receive information collected in conjunction with the co-branded services.
TPC collects and uses your personal contact information to operate paintsquare.com and deliver the services you have requested. These services may include the display of customized content and advertising based upon the information paintsquare.com has collected. TPC does not collect sensitive personal information, such as gender, race, religion, or political affiliations.
TPC may use your personal information to inform you of other products and services available from our company and its affiliates. You may also be consulted about current or potential new products or services that our company may offer.
From time to time, once you've become a member of the PaintSquare community, TPC will send you information about our e-books, webinars, and other technical resources, as well as product information on behalf of our sponsors. Additionally, when you click on advertising hyperlinks in PaintSquare News and on the PaintSquare website, we will provide your contact details to advertisers so they may follow up on the interest you've expressed in their products or services. You may choose to not have your contact details shared with advertisers.
We occasionally hire other companies to provide limited services on our behalf, such as handling the processing and delivery of publication mailings, providing customer support, processing transactions, or performing statistical analysis of our services. We will only provide those companies the personal information they need to deliver the service. They are required to maintain the confidentiality of your information and are prohibited from using that information for any other purpose, in accordance with all current global data protection regulations.
TPC may access and/or disclose your personal information if required to do so by law or in the good faith belief that such action is necessary to: (a) conform to the edicts of the law or comply with legal process served on TPC or the site; (b) protect and defend the rights or property of TPC, including its paintsquare.com website; or (c) act under exigent circumstances to protect the personal safety of users of TPC services or members of the public.
Personal information collected on this site may be stored and processed in the United States or any other country in which TPC or its affiliates, subsidiaries or agents maintain facilities; by using this site, you consent to any such transfer of information outside of your country.
As part of this agreement, you are also providing TPC with the authorization to send you information regarding its products and services via fax if you choose to provide us with your fax number.
TPC offers its customers choices for the collection, use and sharing of personal information. You may choose not to receive marketing material from TPC or on behalf of third-party business partners. You may also stop the delivery of future promotional email from TPC by following the specific instructions in the email you receive. These instructions explain how to stop receiving such emails.
You may subscribe and unsubscribe to TPC newsletters. Each TPC newsletter you receive will include prominently displayed instructions on how to unsubscribe.
TPC operates in compliance with all current global data protection laws, including the General Protection Data Regulation (GDPR). Under this regulation, all users from protected countries have the right to subject access requests (SARs) regarding their personal data collected by TPC.
SARs from individuals should be made by email to webmaster@paintsquare.com. The first SAR for an individual will be provided free of charge. Subsequent SARs from an individual within a 12-month period will be charged USD15 per additional SAR.
TPC will aim to provide the relevant data within 14 days. TPC will always verify the identity of anyone requesting this data before providing any such information.
TPC is committed to protecting the security of your personal information. We use a variety of security technologies and procedures to help protect your personal information from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. For example, we store the personal information you provide on computer systems with limited access, located in controlled facilities. All internal and external sites that process personal information are encrypted through a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol.
PaintSquare.com uses "cookies" to help you personalize your online experience. A cookie is a text file that is placed on your hard disk by a web page server. Cookies cannot be used to run programs or deliver viruses to your computer. Cookies are uniquely assigned to you and can only be read by a web server in the domain that issued the cookie to you.
One of the primary purposes of cookies is to provide a convenience feature to save you time. For example, a cookie helps paintsquare.com to recall your specific information on subsequent visits. This simplifies the process of recording your personal information, such as your username and password. When you return to paintsquare.com, the information you previously provided can be retrieved, so you can easily use the paintsquare.com features to which you subscribe.
You have the right to accept or decline cookies. If you choose to decline cookies, you may not be able to experience all interactive features of the TPC online services or websites you visit. Further, if you choose to decline cookies, TPC will issue one cookie that contains no personal information in order to remember your chosen option.
PaintSquare.com web pages may contain electronic images known as web beacons -- sometimes called single-pixel gifs -- that allow TPC to count users who have visited those pages and to deliver co-branded services. TPC may include web beacons in promotional email messages or paintsquare.com newsletters to count how many messages have been opened and acted upon.
Web beacons collect only a limited set of information, including a cookie number, time and date of a page view, and a description of the page on which the web beacon resides. Web pages at other TPC websites may also contain web beacons placed there by third parties to compile aggregated statistics and to help determine the effectiveness of our joint promotional or advertising campaigns. TPC prohibits third-party web beacons from being used to access your personal information.
The majority of the online banner advertisements you see on paintsquare.com web pages are displayed by TPC.
In addition, TPC may allow other companies, called third-party ad servers or ad networks, to display advertisements on TPC web pages. Some of these ad networks may place a persistent cookie on your computer. Doing this allows members of the ad network to recognize your computer each time they send you an online advertisement. In this way, ad networks may compile information about where you, or others who are using your computer, saw their advertisements and determine which ads have been clicked. This information allows ad networks to deliver targeted advertisements that they believe will be of most interest to you. TPC does not have access to or control of the cookies that may be placed by the third-party ad servers or ad networks.
This PRIVACY NOTICE FOR CALIFORNIA RESIDENTS supplements the information contained above and applies solely to visitors, users, and others who reside in the State of California ("consumers" or "you") when you visit the paintdquare.com website or subscribe to receive the paintdquare.com services (collectively, our "Services"). We adopt this notice to comply with the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 ("CCPA") and other California privacy laws. Any terms defined in the CCPA have the same meaning when used in this notice.
Information We Collect
We collect information that identifies, relates to, describes, references, is capable of being associated with, or could reasonably be linked, directly or indirectly, with a particular consumer or device ("personal information"). In particular, we have collected the following categories of personal information from consumers within the last twelve (12) months:
We collect this personal information from you and from other categories of sources such as: our affiliates; our customers; public and publicly available sources; our third-party vendors, data suppliers and service providers; partners with which we offer co-branded services or engage in joint event or marketing activities; social networks; news outlets and related media; and the organization with which you are employed or affiliated.
We share this personal information with: our affiliates; our customers; our vendors, service providers, suppliers, agents and representatives; joint venture partners; other entities offering products and services that may be of interest to you; the administrators authorized by your organization (if you access our services through a subscription administered by your organization); and other parties where required by law or to protect our rights.
We may use this personal information to operate, manage, and maintain our business, to provide our products and services, to communicate with you, for our vendor management purposes, and to accomplish our business purposes and objectives, including, for example, using personal information to: develop, improve, repair, and maintain our products and services; process or fulfill a request or other transactions submitted to us; personalize, advertise, and market our products and services; conduct research, analytics, and data analysis; maintain our facilities and infrastructure; undertake quality and safety assurance measures; conduct risk and security control and monitoring; detect and prevent fraud; perform identity verification; perform accounting, audit, and other internal functions; comply with law, legal process, and internal policies; maintain records; exercise and defend legal claims; and fulfill legal obligations.
Personal Information Disclosed
We disclose the following categories of personal information to our affiliates; our customers; our vendors, service providers, suppliers, agents and representatives; joint venture partners; other entities offering products and services that may be of interest to you; resellers, distributors, referral partners and integrators; the administrators authorized by your organization (if you access our services through a subscription administered by your organization); licensors of third-party applications (if you access a third-party application on our services through a license agreement with the licensor); and other parties where required by law or to protect our rights for our operational business purposes:
Technology Publishing/PaintSquare.com does not sell personal information to third parties within the scope of the application of the CCPA.
Consumer Rights
You have the right to request that we disclose to you (i) the categories of personal information we collected about you and the categories of sources from which we collected such information; (ii) the specific pieces of personal information we collected about you; (iii) the business or commercial purpose for collecting personal information about you; and (iv) the categories of personal information about you that we shared or disclosed and the categories of third parties with whom we shared or to whom we disclosed such information in the preceding 12 months. You also have the right to request that we delete personal information we collected from you subject to certain exceptions.
You also have the right to not be discriminated against in pricing and services because you exercise any of your rights under the CCPA. TPC does not offer financial incentives or price or service differences to consumers in exchange for the retention or sale of a consumer's personal information.
How to Make a Request
Requests for disclosures or deletion described above may be made by email to webmaster@technologypub.com.
You may be required to submit proof of your identity for these requests to be processed as a verifiable consumer request. We may not be able to comply with your request if we are unable to confirm your identity or to connect the information you submit in your request with personal information in our possession. You may designate an authorized agent to make a request on your behalf subject to proof of identity and authorization.
We will respond to your request consistent with the CCPA, which does not apply to certain information, such as information made available from government records, certain data subject to the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) and certain other laws, and where its application is preempted by, or in conflict with, federal law or the United States or California Constitution.
Changes
We will update this CCPA Notice as part of our overall privacy policy from time to time. Any changes will be posted on this page with an updated revision date.
If you have any questions regarding this statement, contact TPC via email.
TPC may occasionally update this Privacy Statement to reflect company and customer feedback. When TPC posts changes to this Statement, you will see the word "updated" next to the Privacy Statement link on the home page of paintsquare.com. If there are material changes to this Statement or to the ways in which TPC will use your personal information, announcement of such changes will be prominently posted on paintsquare.com prior to their implementation. TPC encourages you to periodically review this Statement to be informed about how TPC is protecting your information.
TPC welcomes your comments regarding this Privacy Statement. If you believe that TPC has not adhered to this Statement, please contact TPC by telephone, email, or postal mail.
Technology Publishing
1501 Reedsdale Street, Suite 2008
Pittsburgh, PA 15233, USA
1-412-431-8300
Goal:
The goal of this policy is to ensure a forum for information, dialogue and fair opinion on relevant issues. The comment function may not be used to promote products, equipment or services or for personal attacks. Posts that violate this policy will be removed.
Specifics:
Consequences for not adhering to policies include the following, not necessarily in this order:
Technology Publishing and PaintSquare reserve the right to alter or remove any content, comments and/or accounts at any time for any reason.











